Introduction
The Filter in Service Maps allows you to refine your view by filtering maps based on their type and availability status. This feature helps you quickly identify specific Service Maps that meet your criteria, enabling efficient monitoring, troubleshooting, and management of your IT environment.
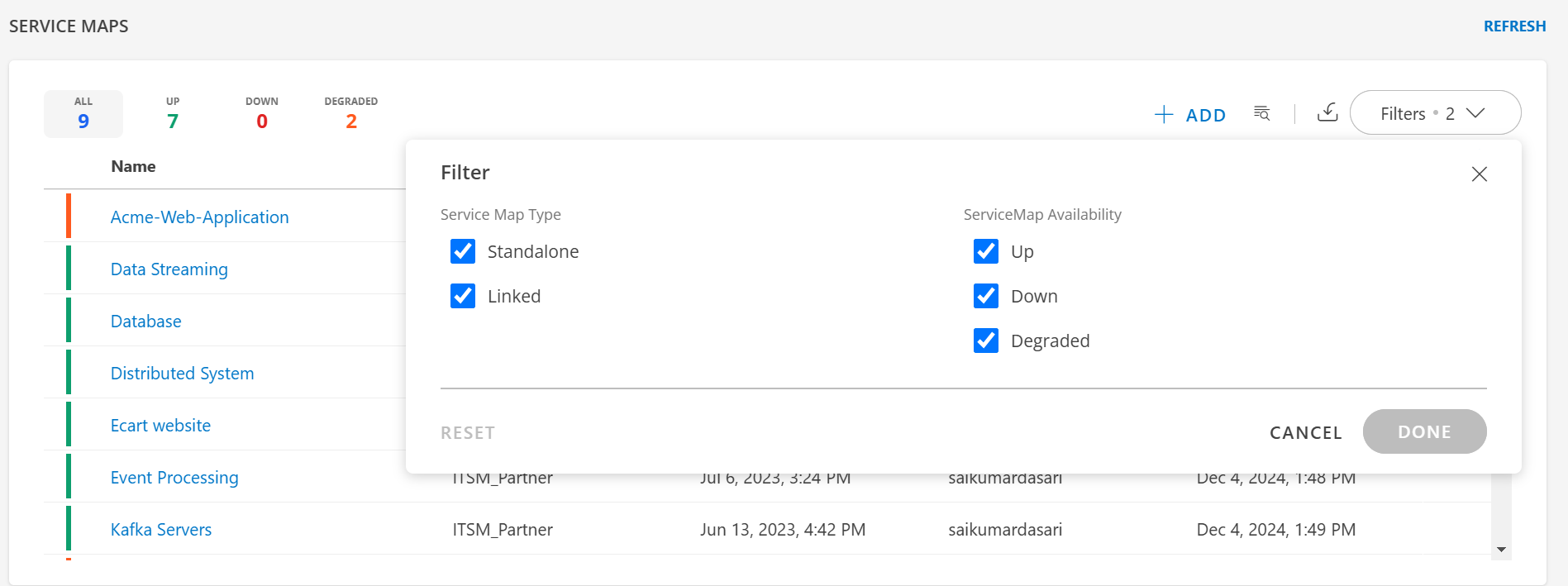
Service Maps Type
Standalone
A self-contained Service Map that represents a single service or application without dependencies on other Service Maps. It is suitable for services or applications that operate independently and do not rely on other business services within the client scope. Example: A Service Map with all the underlying components created in single map.
Linked
A Service Map that links to another existing Service Map, dynamically reflecting real-time updates from the linked map. It is suitable for interconnected services or applications that share resources across multiple maps. Example: A Service Map for a supply chain system linked to an inventory service map, reflecting changes as they occur.
Service Map Availability
Up
Highlighted in Green, it indicates that all components (nodes) in the Service Map are operating normally, with no issues detected. It ensures that the mapped service is fully functional and operational. Example: All application servers, databases, and infrastructure components are running as expected, maintaining service integrity.
Down
Highlighted in Red, it indicates that one or more critical components in the Service Map are non-functional, causing a service disruption. It alerts you to immediate issues requiring troubleshooting to restore the service. Example: A database server in the Service Map is unresponsive, causing the service to go offline.
Degraded
Highlighted in Amber, it indicates that some components of the Service Map are experiencing issues, but the service is partially operational. It helps identify performance bottlenecks or non-critical issues impacting the service. Example: A load balancer is experiencing latency, slowing traffic but not fully disrupting the service.